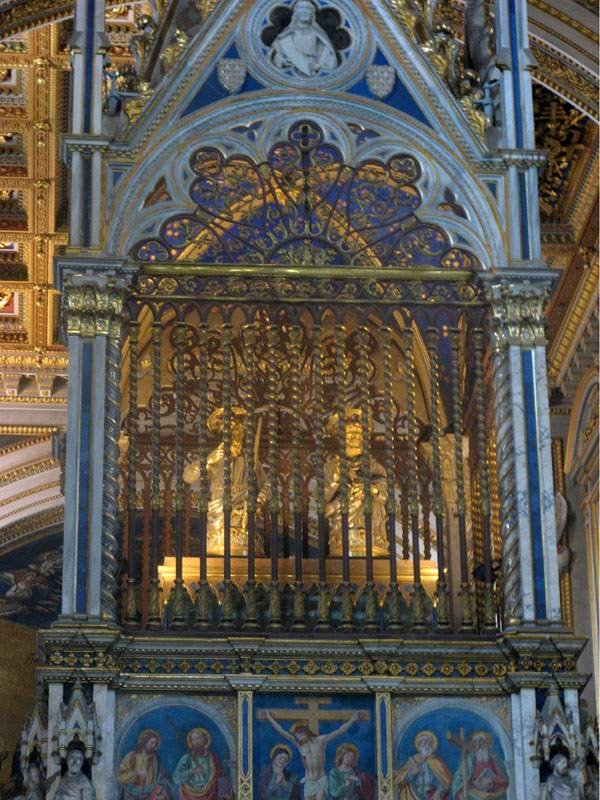
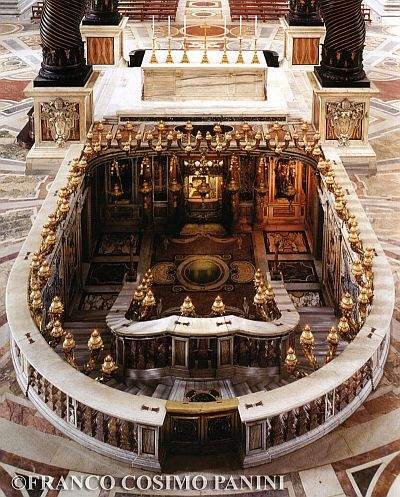
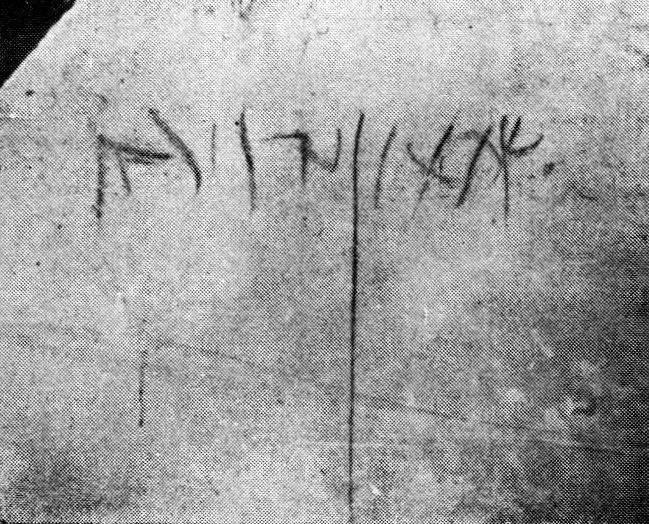The past few days, since Pope Francis put some of the relics of St. Peter on display, my blog hits have spiked again. A number of news outlets picked up images from my posts on the Tomb of St. Peter in Rome and linked back here. And this topic continues to fascinate the public as it always has (those posts are by far my most popular) — because, I reckon, the public is just fascinated by bones. Especially long-buried bones. Especially mysterious, even controversial bones. And about that controversy: Coming from the camp of the very same anti-Catholics who seek to argue that St. Peter was never in Rome, there is a claim floating around of a supposed tomb of St. Peter discovered in Jerusalem in 1953 which, if known, would undermine the whole foundation of the Catholic Church and expose the Vatican as a fraud, etc.
There’s one problem, though: the claim itself is a fabrication. The linked article is taken from the pages of a 1971 anti-Catholic tract, self-published by one F. Paul Peterson of Fort Wayne, Indiana, and sold from his home. It is poorly written and rife with factual errors (e.g. the Saracens “never made it to Rome”), unfounded accusations, and unsubstantiated claims. In a tract which purports to provide solid evidence of the burial of the Apostle Peter in Jerusalem, the author actually provides little real evidence other than his own testimony that various people, including a number of well known archaeologists and even Pope Pius XII, agree with him regarding his remarkable discovery and its implications. This is little more than a baseless screed like so much of the anti-Catholic literature out there, akin to Chick tracts and even making similar claims. I normally would not waste my time in responding, but for my concern that this web page is among the top hits on Google for the “tomb of St. Peter.” Anti-Catholics will believe anything — but for anyone out there who is honestly seeking answers, I do not want them to be misled.
For anyone who wants to critically examine this claim of a supposed tomb of Peter in Jerusalem, and the claims of the Catholic Church, here are a few points to consider — just a few of the major problems with this article:
-
The author claims repeatedly that there is “no evidence in either Scripture or history” that Peter was ever in Rome — but clearly either he has not read much history, or he is willfully distorting the truth. I have repeatedly provided evidence, from both Scripture and history. And if one finds Scripture less than explicit, the historical testimony is well documented and compelling.
In fact, there is a unanimous historical tradition that Peter died and was buried in Rome (from Latin trado, trans + do, “to hand over” or “hand down”) — meaning not something vague and “fickle” as Peterson alleges, but attested fact handed down by generation after generation of writers, dating with certainty to the early second century, in all likelihood to within a few years of Peter’s death — and not by “Roman” writers, but by partisans of the Churches of Antioch (e.g. Ignatius), Alexandria (e.g. Clement), Carthage (e.g. Tertullian), and many other scattered places, who would have had no reason to fabricate facts in Rome’s favor. Meanwhile there is no tradition, no testimony, absolutely none, that Peter remained in Jerusalem following the events of the New Testament and died there; no record or attestation or claim that Peter’s tomb ever existed in Jerusalem until this supposed “discovery” came out of nowhere (and in fact never really went anywhere: Peterson’s tract has no doubt had thousands more readers on the Internet than it ever had in his lifetime). While Christians the world over celebrated the tombs and relics of martyrs scattered all over the Mediterranean world and beyond — in some cases no doubt inventing them — no one ever claimed that Peter was in Jerusalem.
Peterson makes repeated statements that are manifestly false, but after reading the piece in depth, I do believe the man is genuine — genuinely ignorant and misled. It being the days before the Internet, I can forgive him for not having ready access to facts; but even today, facts do not get in the way of anti-Catholic delusions.
-
He alleges throughout the piece that there has been a conspiracy to “[put] a smoke screen around the truth” that St. Peter is in fact buried in Jerusalem, reaching to the highest levels of the Catholic hierarchy, to Pope Pius XII; that there are “secrets” in the Vatican that somehow only he is privy to. He envisions himself as the hero who will bring the “truth” to the world:
Having succeeded for so long in keeping ‘this thing quiet,’ … they [Catholics] were off guard when a fellow at that time came along who appeared harmless but persistent. Little did they know that this fellow would publish the news everywhere. Their position in the world is shaky enough without this discovery becoming generally known.
-
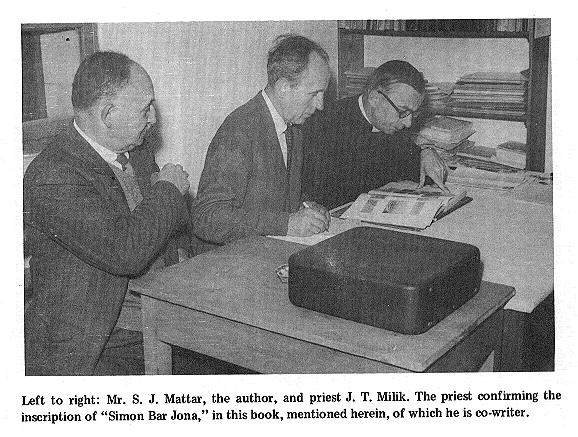
He purports to have visited “various renowned archaeologists” to discuss this subject, several of whom he names, and who were indeed renowned archaeologists — William F. Albright (of whom he did not give the full name, only referring to “Dr. Albright of John Hopkins [sic] University”), Nelson Glueck, Józef Milik, Bellarmino Bagatti — each of whom supported and agreed with his unquestionable evidence — and yet none of these renowned archaeologists, in all their well-read and respected works, thought this earth-shattering revelation was worthy of wide publication. Somehow F. Paul Peterson remains the only one who can reveal this news. (He suggests that “Dr. Gluek, being Jewish, is not fully aware … that such a discovery is very embarrassing since it undermines the very foundation of the Roman Catholic Church.”)
-
The latter two archaeologists, Bagatti and Milik, in fact did publish on this matter, Peterson claims. He claims they published a book in Italian, Gli Scavi del Dominus Flevit, which reveals the truth of the tomb of Peter in Jerusalem. But somehow this academic work published by two renowned archaeologists has escaped the notice of not only the archaeological community, but of the entire world, until it was discovered by one F. Paul Peterson of Fort Wayne, Indiana. And this suppressed, forgotten archaeological publication, in which these archaeologists, according to the author, state unequivocally that St. Peter is buried in Jerusalem, not Rome, is so obscure that several thousand books in the Google Books catalog cite it. And yet somehow everyone who reads and cites this work overlooks this astounding revelation.
He also cites numerous unnamed priests and archaeologists who agreed with his evidence: a “highly educated priest,” “a brilliant American priest in Rome,” etc.
-
The claim is that this supposed Jerusalem tomb of Peter was discovered during the excavations of Bagatti and Milik of the ancient Christian necropolis under the Church of Dominus Flevit (“The Lord wept”) on the Mount of Olives (this is the subject of the above mentioned book, per the title). And yet this is now a well-known tourist attraction and site of pilgrimage, and everyone neglects to mention the irrefutable evidence that the Apostle Peter was buried there.
-
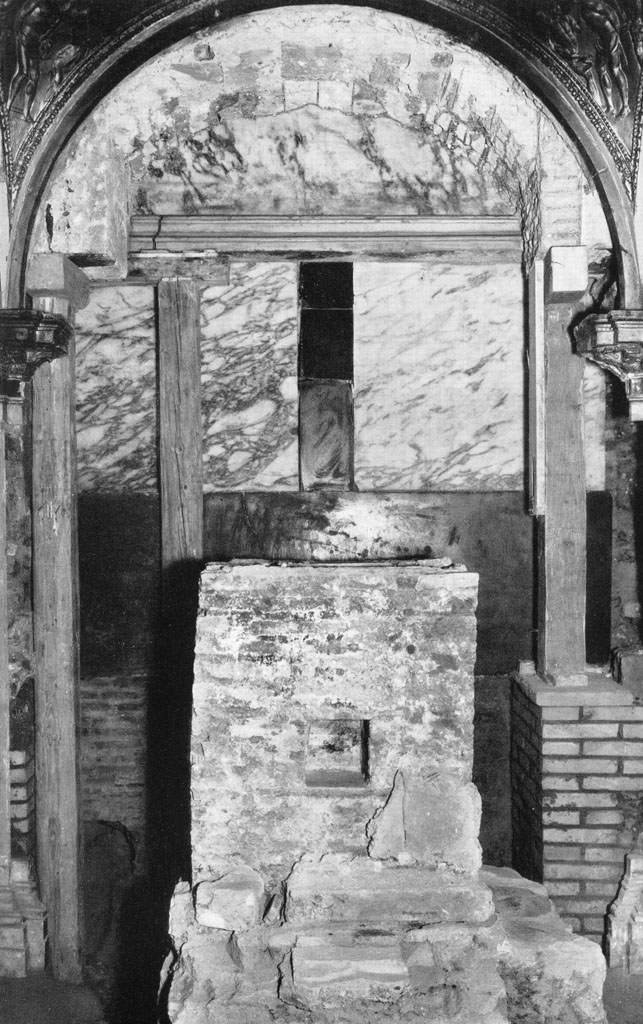
The only “solid evidence” which Peterson provides — which “a person who has seen … could never doubt that this truly is the burial place of St. Peter” — is solely that the inscription on an ossuary appeared to read in Aramaic, “Simon bar-Jona.” Yet the names “Simon” (שמעון) and “Jona” (יוֹנָה) or “John” (יוֹחָנָן) are all among the most common Jewish names. Finding a tomb marked “Simon son of Jona” in Jerusalem is no more significant than finding a grave in London marked “John Smith.” That it is an early Christian grave is certainly interesting — because it’s an early Christian grave, not because it is that of Simon Peter.
-
In fact, Fr. Bagatti did publish regarding the tomb in question — not in Gli Scavi del Dominus Flevit, but in an academic journal, Liber Annuus — and it did briefly cause some concern. But rather than shaking the Vatican to its knees, nothing came of the matter. The evidence was considered ambiguous and inconclusive, and not worthy of public attention; certainly it was not “suppressed” or “hidden.” When Milik completed the publication of Gli Scavi del Dominus Flevit, he in fact equivocated on the reading. Nothing in the book makes the bold claim that this was the tomb of the Apostle Peter.
The author of this webpage, not the same anti-Catholic who wrote the article, has posted some scans of pages from Gli Scavi del Dominus Flevit which supposedly prove the claims. But the text says nothing of the sort. In the page purportedly describing the inscription, Milik wrote:
11. locus 79, ossuary 19. In the upper corner on the long side, confidently sketched using charcoal with very fine features; name (length. cm. 9,5; letters 11 – 0,8 – 1,5), fot. 81 and fig. 22,1):
. . . שמעון בר [Simeon bar …]
The reading of the patronym, as luck would have it, is uncertain. The reading proposed in Liber Annuus III, p. 162 (יונה [Jonah]) [this is Bagatti’s article] remains possible, but other possibilities for it can equally be proposed, such as זינה [zinh] correspondent to Ζηνα [Greek Zēna] of n. 21. The two cases of a supposed [Hebrew letter] nun are both a little unusual and the [Hebrew letter] he is rather abnormal although it has an affinity to “Palmyrene”. Alternatively, these last two letters can be considered as a single one, that is, a he with a bifurcated left leg, that would have been inexpertly executed with a piece of charcoal; notice the double feature in the charcoal tracings in fig. 22,7 and 6; fot. 80; LA VII, p. 247, fig. 16. In this case it would have to be read זיה [zih], זוה [zoh], etc.
The writing is cursive. The [Hebrew Letter] shin was made with charcoal by a single stroke; Another unique feature is the curves of the [Hebrew letter] mem and of [Hebrew Letter] 'ain, like a cross formed from two oblique features; [Hebrew letters] beth + resh is a ligature.
On the frequency of this name Simeon, see n. 5.
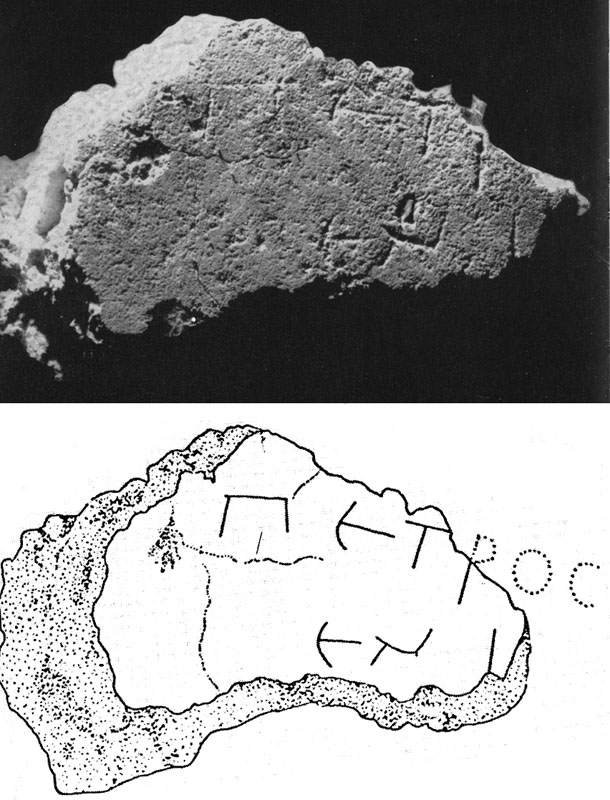
- This reading itself has been disputed. A fascinating article by Dr. Stephen Pfann of the University of the Holy Land is available online: “Has St. Peter returned to Jerusalem? The final resting place of Simon Peter and the family of Barzillai.” F. Paul Peterson, it seems, is not the only one to have dredged up such a concoction of this charge. It was also featured in the documentary The Lost Tomb of Jesus, in which a hack archaeologist similarly discovered a tomb in Jerusalem marked with the names of Yeshua, Yosef, Miriam (Jesus, Joseph, Mary) — and made the claim we have all heard by now, despite these three names likewise being among the most common Jewish names. Pfann convincingly argues that the ossuary at Dominus Flevit reads “Simeon bar Zilla” — denoting the family of Barzillai, a “Jerusalem family [with] deep roots within Biblical history.”
Herein, lies the greatest proof that Peter never was a Pope, and never was in Rome, for if he had been, it would have certainly been proclaimed in the New Testament. History, likewise, would not have been silent on the subject, as they were not silent in the case of the Apostle Paul. Even the Catholic history would have claimed the above as a fact and not as a fickle tradition.1 To omit Peter as being Pope and in Rome (and the Papacy) would be like omitting the Law of Moses or the Prophets or the Acts of the Apostles from the Bible.
Usually a Catholic, either because he is brainwashed or stubbornly doesn’t want to see anything against what he has been taught, will not allow himself to believe anything against his religion, much less admit it to others. But there is a growing, healthy attitude among many Catholics, to ‘prove all things, hold fast to that which is good’ as the Master admonished us all.
The secrecy surrounding this case is amazing, yet understandable, since Catholics largely base their faith on the assumption that Peter was their first pope and that he was martyred and buried there.
People who lived in Jerusalem all their lives and official guides who are supposed to know every inch of the city, however, knew nothing of this discovery, so well was it withheld from the public.
These figures go along perfectly, as does everything else in the case, with the remains found in the Christian burial ground on the Mount of Olives and in the ossuary on which was ‘clearly and beautifully written,’ Simon Bar Jona in Aramaic.

Page 83 of Gli Scavi del Dominus Flavit, purportedly describing this ossuary as that of the Apostle Peter (translation below).
If there remained any doubt that this supposed “Jerusalem tomb of Peter” is not the “indisputable proof” that the Catholic Church is a fraud, or that it is what anti-Catholics have claimed it is, I hope I have dispelled it.
Quickly, before I let you go, I wanted to share a few more priceless claims from Peterson’s article:
-
“Eusebius, one of the most learned men of his time, wrote the Church history up to the year 325 A.D. He said that Peter never was in Rome.1 This Church history was translated by Jerome from the original Greek, but in his translation he added a fantastic story of Peter’s residence in Rome.2 This was a common practice in trying to create credence in their doctrines, using false statements, false letters and falsified history. This is another reason why we cannot rely on tradition, but only on the infallible Word of God.”
1 N.B. Eusebius states numerous times that Peter was in Rome. —JTR2 N.B. The original Greek of Eusebius states that Peter was in Rome. —JTR -
“Mark you, all the priests agree that the Vatican and St. Peter’s were built over a pagan cemetery.1 This was a very appropriate place for them to build since, as even Cardinal Newman admitted, there are many pagan practices in the Roman Catholic Church. You realize surely, that Christians would never bury their dead in a pagan cemetery, and you may be very sure that pagans would never allow a Christian to be buried in their cemetery.”
1 N.B. All cemeteries were pagan cemeteries in first-century Rome, until Christians began to bury in the catacombs in the second or third century. There’s every indication that Peter’s burial in this cemetery, as well as the veneration of the tomb over the cemeteries, was secret and surreptitious. By the time of the cemetery’s destruction and the construction of St. Peter’s Basilica, the cemetery had increasing numbers of Christian burials. —JTR -
“Strange it was, for since beginning to build the church in 1450 (finished in 1626)1 they erected, St. Peter’s Tomb (?) under the large dome and Bernini’s serpentine columns. Since then multiplied millions were thereby deceived into believing that the remains of St. Peter were there, which the hierarchy had all along known was not true, as is proven by the late Pope’s [Pius XII’s] declaration.”
1 N.B. The original St. Peter’s Basilica was begun between 326 and 331. The Church did not suddenly claim in 1450 that Peter was buried on the Vatican under a newly-constructed church. —JTR
I feel rather sorry for Mr. Peterson. Reading his article, I get the sense that he was a good and honest man who sincerely believed (most of) what he was writing. Without a doubt, though, he was stretching the facts quite far in his claims of archaeologists and popes affirming him in his evidence. I sincerely hope this wasn’t him (the only F. Paul Peterson I could find in Indiana).